Difference between revisions of "IBH Link UA:Python/Methods/Data models"
m (→Visual Studio Code) |
m (→Visual Studio Code) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
[[Image:IBH_Link_UA_Nodeset.png|504px]] | [[Image:IBH_Link_UA_Nodeset.png|504px]] | ||
| − | + | == Visual Studio Code== | |
To obtain a convenient code autocompletion in Visual Studio Code, the definition file ibhua.pyi can be copied into the working directory.<br> | To obtain a convenient code autocompletion in Visual Studio Code, the definition file ibhua.pyi can be copied into the working directory.<br> | ||
'''[http://download.ibhsoftec.com/neutral/ibhua.pyi.zip ibhua.pyi]''' | '''[http://download.ibhsoftec.com/neutral/ibhua.pyi.zip ibhua.pyi]''' | ||
Latest revision as of 12:37, 14 March 2024
This option is only activated in the IBH-Link-UA-QC, as more memory is required to execute Python functions.
Methods can now be realized with the Python programming language and data can be exchanged and processed more easily.
Some examples of the implementation of complex functions:
- Complex tasks can be automated, such as the monitoring of machine parameters or the optimization of production processes.
- Large amounts of data can be analyzed and evaluated in order to identify trends and patterns to optimize processes.
Contents
Structure of a Python program
The special functions of the IBHLinkUA are imported in the Python program. For initialization, the IBHLinkUA calls the function "init_opc()". Example:
import ibhua
def init_opc(): return
Several Python programs can be read in. Python programs without these special functions are also possible.
Visual Studio Code
To obtain a convenient code autocompletion in Visual Studio Code, the definition file ibhua.pyi can be copied into the working directory.
ibhua.pyi
Functions from the ibhua module
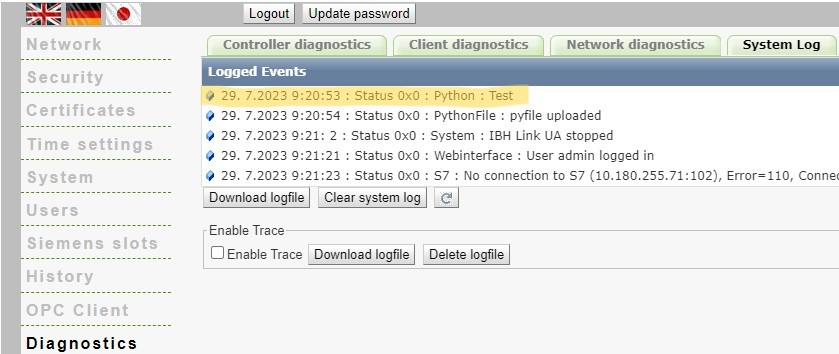
RedirectLogOutput()
Redirects all print, stdout and stderr outputs to the system log. This can be viewed in the web interface under "Diagnostics - System Log".
Example:
import ibhua
ibhua.RedirectLogOutput()
def init_opc():
print("Test")
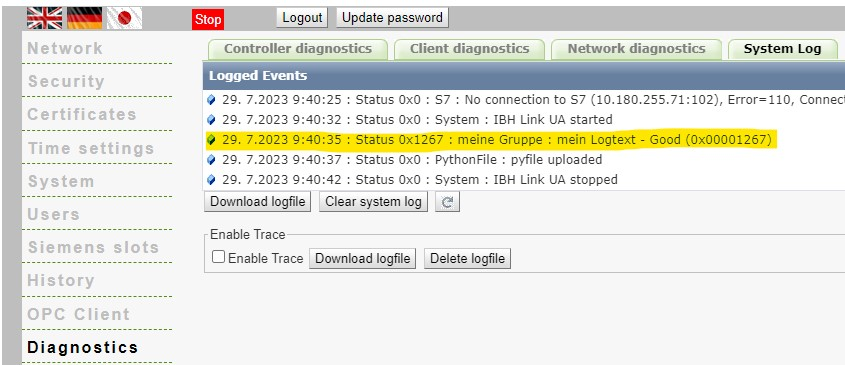
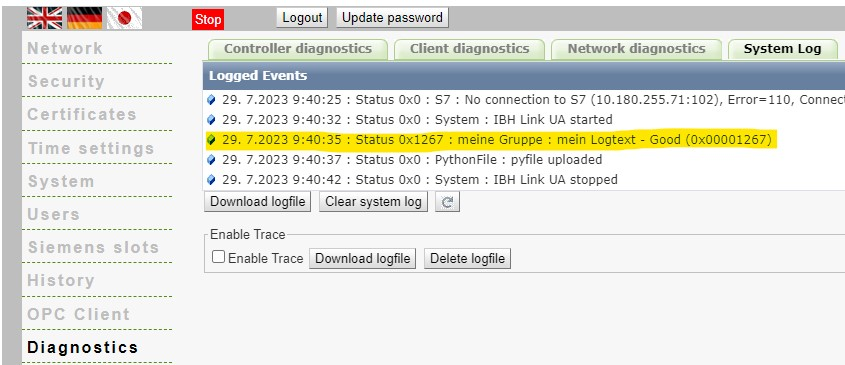
setSystemLog (Group,logtext,status)
Writes an entry to the system log. This can be viewed in the web interface under "Diagnostic system events". Parameter:
- Group : String - logtext : String - Status : Integer
Example:
import ibhua
def init_opc():
ibhua.setSystemLog("my Group","my Logtext",4711)
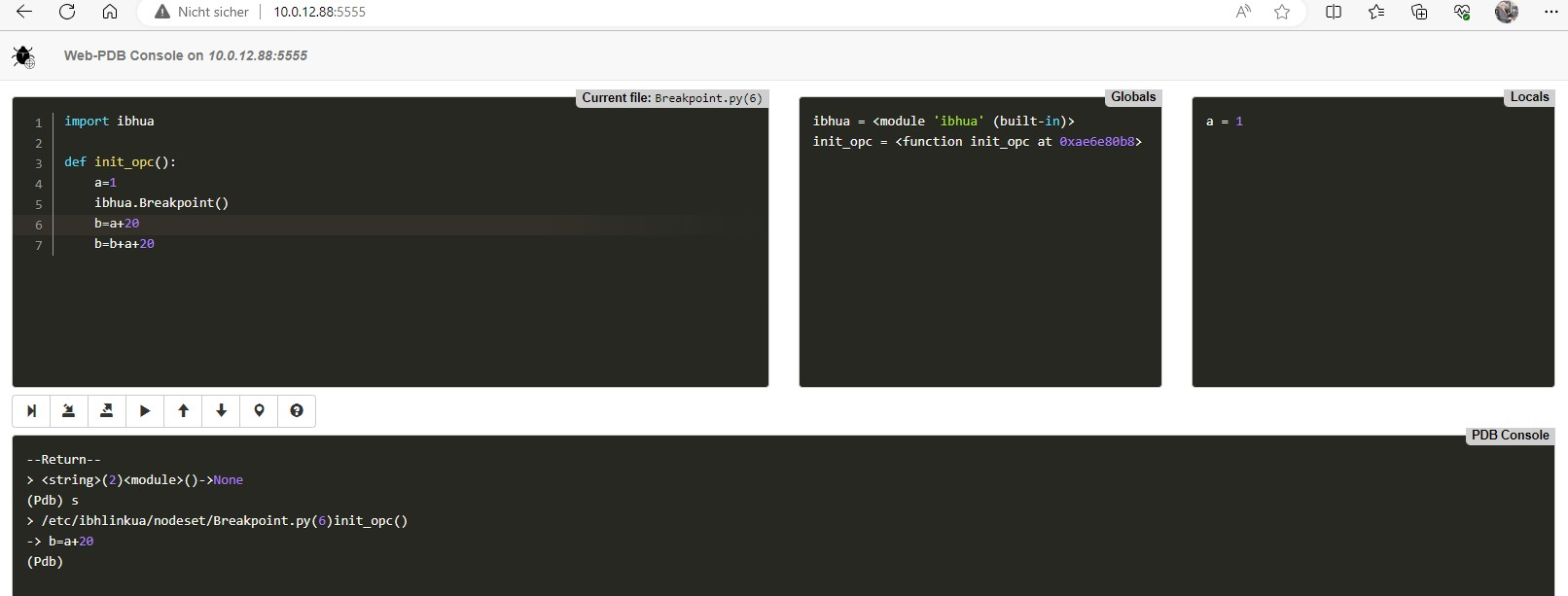
Sets a breakpoint. When the breakpoint is reached, the debugger is activated.
The debugger can be accessed via a web browser using port 5555.
Example:
import ibhua def init_opc(): a=1 ibhua.Breakpoint() b=a+20 b=b+a+20
After loading the example:
After pressing the Step button:
OPCReadVar(node)
Function for reading OPC nodes.
Parameter:
- node: Nodeid
- Return value: Scalar value or string variable
Examples:
import ibhua
ibhua.RedirectLogOutput()
def init_opc():
clock=ibhua.OPCReadVar("ns=0;i=2258")
print(clock)
In this example, the current time is entered in the diagnosis after the restart.
monitor("node", "Monitor Function", Interval, Triggermode, Deadband)
When the OPC variable "Node" is changed, the "Monitor function" is called.
Interval: determines the sampling interval in ms.
„Triggermode“ :
- 0 = is always triggered
- 1=Trigger on value change
- 2=Trigger on rising edge
- 3=Trigger on falling edge
Deadband: determines the minimum value change that leads to the trigger
The monitor function contains an input parameter with the read value.
Example:
import ibhua
ibhua.RedirectLogOutput()
def Monitor(Var):
print(Var)
return
def init_opc():
ibhua.monitor("ns=0;i=2258","Monitor",1000,0,0)
return
In this example, the current time is entered in the diagnosis every second.
OPCWriteVar(node,var)
Function for writing scalar nodes and string nodes. The OPC type is automatically determined from the target variable.
Parameter:
- node: Nodeid
- var: Scalar oder String value
Example:
import ibhua
def Monitor(Var):
ibhua.OPCWriteVar("ns=4;s=QuadcoreNodesetExample.SoftPLC.Generic.ActualWatch",Var)
return
def init_opc():
ibhua.monitor("ns=0;i=2258","Monitor",1000,0,0)
return
In this example, the time is entered every second in the PLC string variable QuadcoreNodesetExample.SoftPLC.Generic.ActualWatch.
OPCResult()
Returns the result of the OPCReadVar, OPCWriteVar and OPCCallMethod functions.
Parameter:
- Returnwert: 0=Successful
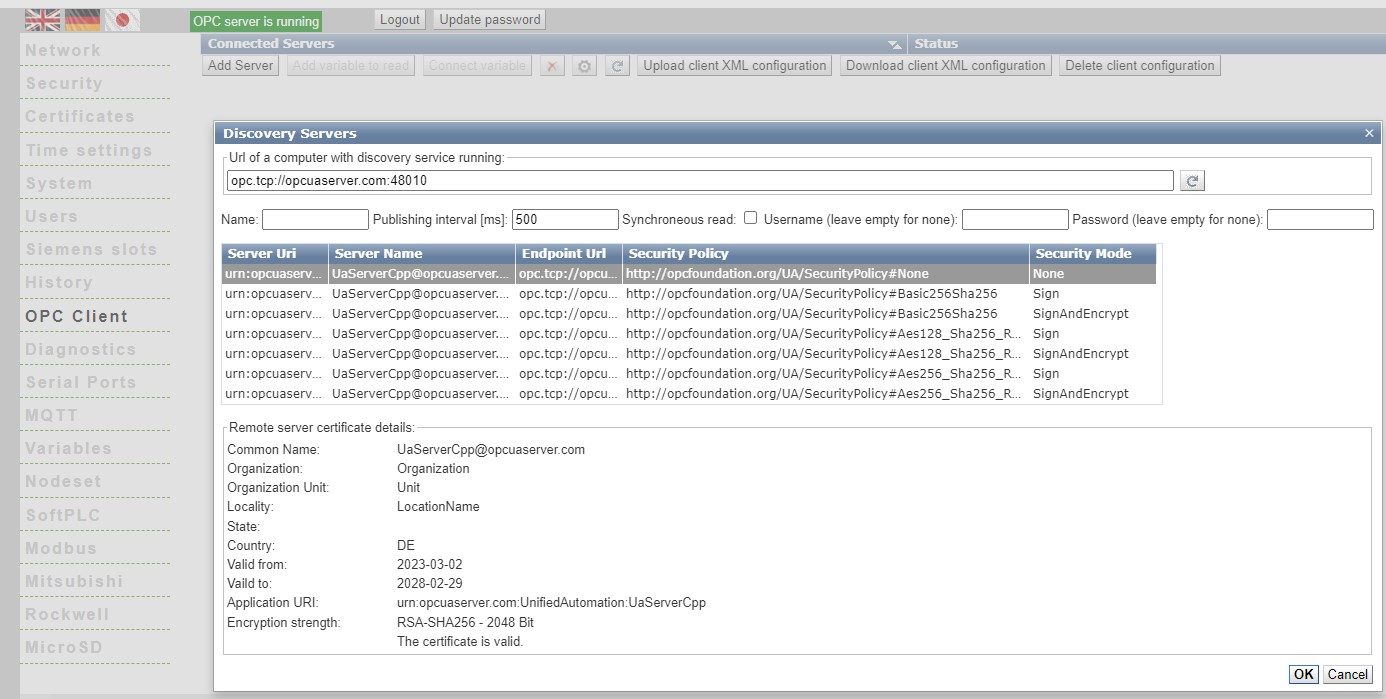
Access to external OPC servers
To access external OPC servers, an external server must first be set up in the client function.
The functions:
OPCReadVar
OPCWriteVar
OPCCallMethod
the server name is specified as the first parameter.
Attention ! The server name must be entered exactly as in the web interface (note the space before the "(") !
Example:
ExternalServer = "urn:ibhlinkua-002808:IBHsoftec:IBHLinkUA (opc.tcp://10.0.12.88:48010)" … OPCVar=ibhua.OPCReadVar(ExternerServer,"ns=4;s=PC-Station.Software PLC_1.GlobalVars.Tag_1")
OPCConnectedServers ()
This function returns a list of the connected OPC servers.
With this function you can easily determine the complete name of an external server.
Example:
In the following examples, it is assumed that you have established a connection to the Unified Automation demo server (opc.tcp://opcuaserver.com:48010) in the client function.
import ibhua
ibhua.RedirectLogOutput()
ExternalServer=""
def init_opc():
#search in ExternalServers "opcuaserver.com"
ExternalServers=ibhua.OPCConnectedServers ()
print (ibhua.OPCConnectedServers ())
for line in ExternalServers:
if "opcuaserver.com" in line:
ExternalServer=line
if ExternalServer:
print (ExternalServer)
else:
print("no external Server")
if ExternalServer:
FillLevelSetPoint=ibhua.OPCReadVar(ExternalServer,"ns=2;s=Demo.BoilerDemo.Boiler1.FillLevelSetPoint")
print(FillLevelSetPoint)
OPCCallMethod(ExternalServer,object-nodeid, method-nodeid)
Calling a method without parameter
Parameter:
- ExternalServer
- object-nodeid : Nodename of the parent object
- method-nodeid : Nodename of the method
- return : Result (0=successful)
Example:
import ibhua
ibhua.RedirectLogOutput()
ExternalServer=""
def init_opc():
#search in ExternalServers "opcuaserver.com"
ExternalServers=ibhua.OPCConnectedServers ()
for line in ExternalServers:
if "opcuaserver.com" in line:
ExternalServer=line
if ExternalServer:
result=ibhua.OPCCallMethod(ExternalServer,"ns=2;s=Demo","ns=2;s=Demo.StartSimulation")
print(result)
OPCCallMethod(ExternalServer,object-nodeid, method-nodeid,[parameter_1,…parameter_n)
Calling a method with parameter:
Parameter:
- ExternalServer
- object-nodeid : Nodename of the parent object
- method-nodeid : Nodename of the method
- [parameter]: Input parameter list
- return Output parameter list
Example:
import ibhua
ibhua.RedirectLogOutput()
ExternalServer=""
def init_opc():
#search in ExternalServers "opcuaserver.com"
ExternalServers=ibhua.OPCConnectedServers ()
for line in ExternalServers:
if "opcuaserver.com" in line:
ExternalServer=line
if ExternalServer:
results=ibhua.OPCCallMethod(ExternalServer,"ns=2;s=Demo.Method","ns=2;s=Demo.Method.Multiply",[2.14,3.5])
status=ibhua.OPCResult()
if status==0:
for result in results:
print(result)
else:
print("Error")
Here is an example that controls a method with parameter from the PLC::
import ibhua
ibhua.RedirectLogOutput()
ExternalServer=""
def Multiply(var):
global ExternalServer
if ExternalServer:
Mul_a=ibhua.OPCReadVar("ns=4;s=QuadcoreNodesetExample.SoftPLC.Generic.Mul_a")
Mul_b=ibhua.OPCReadVar("ns=4;s=QuadcoreNodesetExample.SoftPLC.Generic.Mul_b")
results=ibhua.OPCCallMethod(ExternalServer,"ns=2;s=Demo.Method","ns=2;s=Demo.Method.Multiply",[Mul_a,Mul_b])
status=ibhua.OPCResult()
if status==0:
for result in results:
ibhua.OPCWriteVar("ns=4;s=QuadcoreNodesetExample.SoftPLC.Generic.MUL_Result ",result)
else:
print("Error")
def init_opc():
global ExternalServer
#search in ExternalServers "opcuaserver.com"
ExternalServers=ibhua.OPCConnectedServers ()
for line in ExternalServers:
if "opcuaserver.com" in line:
ExternalServer=line
ibhua.monitor("ns=4;s=QuadcoreNodesetExample.SoftPLC.Generic.StartMul","Multiply",1000,2,0)
Working with nodesets
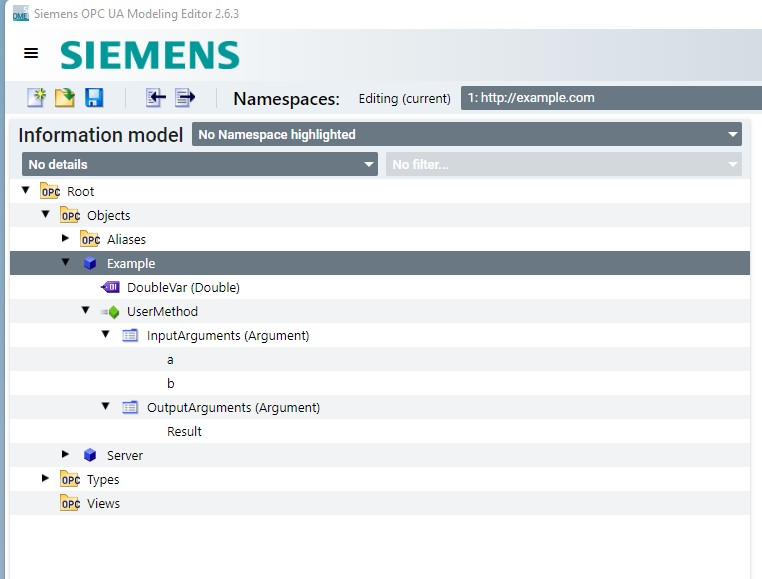
It is now possible to read in nodesets and link them to Python modules.
The nodesets are created with UAModeler or SiOME (freeware from Siemens).
The project is an output as an XML file in the modeller.
You can find documentation on the SiOME here: https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/document/109755133/siemens-opc-ua-modeling-editor-(siome)?dti=0&lc=de-DE
The manual can be found here: https://support.industry.siemens.com/cs/attachments/109755133/109755133_SiOME_MAN_V27_de.pdf
Execute "Modelling the address space" according to the manual and export the information model (3.19):
Load the information model
The created object then appears in the address space of the OPC server:
Now the variables and methods can be linked to the Python program.
OPCError (OPC error code)
Cancels execution if the error code is not 0 and returns the OPC error code.
If a 0 is passed, the function has no effect.
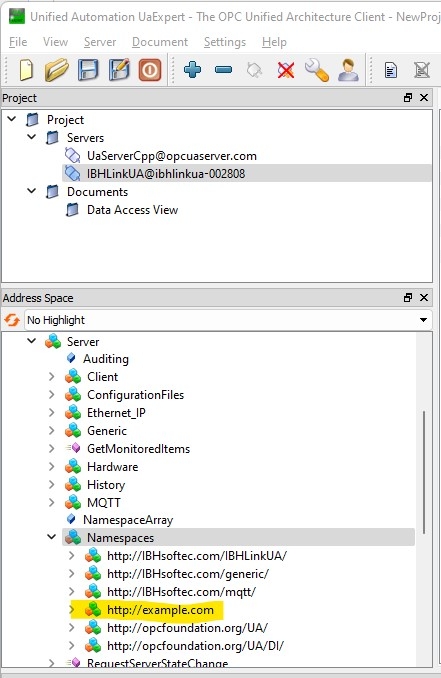
get_namespace(name)
This function returns the namespace number. The namespace name is specified as the input parameter.:
Example:
import ibhua
ibhua.RedirectLogOutput()
def init_opc():
ns=ibhua.get_namespace("http://example.com")
print(ns)
method(ns, id, "function")
Links a method defined in an imported nodeset with a Python function.
Parameter: * ns : Namespace number * Id : Nodename or Numeric ID * OPC function, that is called with the method
The function contains an argument for each input parameter and can return an argument for each output parameter.
Functions without an output parameter may not return a value.
The function result (success/failure) must generally be transferred with OPCError().
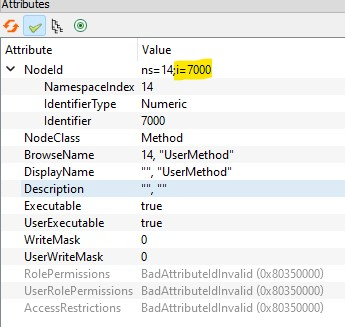
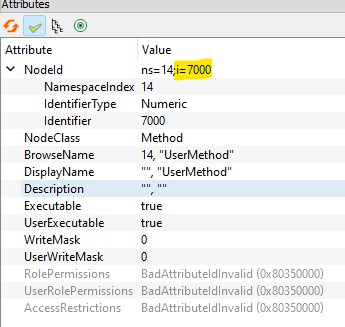
id can be determined with the UAExpert :
Example:
import ibhua
ibhua.RedirectLogOutput()
def UserMethod(a,b):
result=0
c=a*b
ibhua.OPCError(result)
return c
def init_opc():
ns=ibhua.get_namespace("http://example.com")
ibhua.method(ns,7000,"UserMethod")
variable(ns, id, "read function", "write function")
Links a variable defined in an imported nodeset with a Python function.
Parameter:
- ns : Namespace number
- Id : Nodename or numeric ID
- read function : Function that is called when the variable is read
The function does not contain an input parameter and one output parameter.
- write function : Function that is called when the variable is written
The function contains one input parameter and no output parameter Example:
import ibhua
OPCVar=123.456
def UserRead():
result=0
global OPCVar
ibhua.OPCError(result)
return OPCVar
def UserWrite(var):
result=0
global OPCVar
OPCVar=var
ibhua.OPCError(result)
return
def init_opc():
ns=ibhua.get_namespace("http://example.com")
ibhua.variable(ns,6008,"UserRead","UserWrite")
map(ns, id, ns_destination, id_destination )
Connects the OPC variable (ns,id) to another variable.
The advantage of this function is that no Python program is run during reading and writing. (faster)
Attention: The data types must match!
Parameter:
- ns : Namespace number
- id : Nodename or numeric ID
- ns_destination : Namespace number of the target variable
- id_destination : Nodename or numeric ID of the target variable
- node : NodeID of the variable in another namespace
- Return value: 1=successful, -1=not successful
Example:
import ibhua
def init_opc():
ns=ibhua.get_namespace("http://example.com")
ibhua.map(ns,6011,4,"QuadcoreNodesetExample.SoftPLC.Generic.PLCFloatVar")
Detailed examples
Example with a S7-1500 PLC
The documentation and examples are provided by our training partner TTI.
Documentation suitable for the example S7-1500 PLC
Example matching the Documentation
The zip file contains Phyton, IBH OPC UA Editor examples and the TIA V18 project
A method from the nodeset executes a function block in the PLC
Python Programm :
import ibhua
import time
#OPC Error Codes
Bad_Timeout=0x800A0000
Bad_UnexpectedError=0x80010000
def SetTemperature(SetPoint):
Method_Control=ibhua.OPCReadVar("ns=4;s=QuadcoreNodesetExample.SoftPLC.GlobalVars.UA_Method_Control")
if Method_Control==0:
ibhua.OPCWriteVar("ns=4;s=QuadcoreNodesetExample.SoftPLC.Programs.DB 1.SetPoint",SetPoint)
ibhua.OPCWriteVar("ns=4;s=QuadcoreNodesetExample.SoftPLC.GlobalVars.UA_Method_Control",1)
Method_Control=1
seconds = time.time()
while Method_Control==1:
Method_Control=ibhua.OPCReadVar("ns=4;s=QuadcoreNodesetExample.SoftPLC.GlobalVars.UA_Method_Control")
if time.time()>(seconds+2):
ibhua.OPCError(Bad_Timeout)
ibhua.OPCWriteVar("ns=4;s=QuadcoreNodesetExample.SoftPLC.GlobalVars.UA_Method_Control",0)
ActualTemperature=Method_Control=ibhua.OPCReadVar("ns=4;s=QuadcoreNodesetExample.SoftPLC.Programs.DB 1.Actual")
else:
ibhua.OPCError(Bad_UnexpectedError)
return ActualTemperature
def ReadTemp():
return ibhua.OPCReadVar("ns=4;s=QuadcoreNodesetExample.SoftPLC.GlobalVars.Temperature")
def init_opc():
ns=ibhua.get_namespace("http://example.com")
print(ns)
ibhua.method(ns,7001,"SetTemperature")
ibhua.monitor("ns=4;s=QuadcoreNodesetExample.SoftPLC.GlobalVars.Temperature","Temperature",1000,0,0)
ibhua.variable(ns,6014,"ReadTemp","")
Extract from the PLC program:
L "UA_Method_Control" // Call Method L 1 <>I SPB noc CALL FB 1, DB 1 SetPoint := Actual := L 2 // Method Complete T "UA_Method_Control" noc: